A blockchain is a digital ledger containing records of all transactions or events, shared among participants. Every transaction is independently verified by most participants in the system. Bitcoin is the most widely used cryptocurrency as an example of a blockchain. In 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto released a white paper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”.
However, Blockchain in the supply chain records transactions in a digital ledger that is shared over the Network, making it untouchable.
Anything of value, such as land assets, cars, etc., can be recorded as a transaction on the blockchain. Business runs on information. That should be received as fast as possible, and the more accurate it is, the better. However, Blockchain is suitable for the dissemination of that information since it offers real-time, simultaneous, and measurable data that resides in a tamper-proof database accessible only to authorized members of the decentralized network. Moreover, an application can also track orders, payment accounts, production and other things on a blockchain network. Since members have a common perspective of the truth, one gets an outlook of the details of a transaction from beginning to end – making it more certain and unveiling new possibilities of efficiencies.
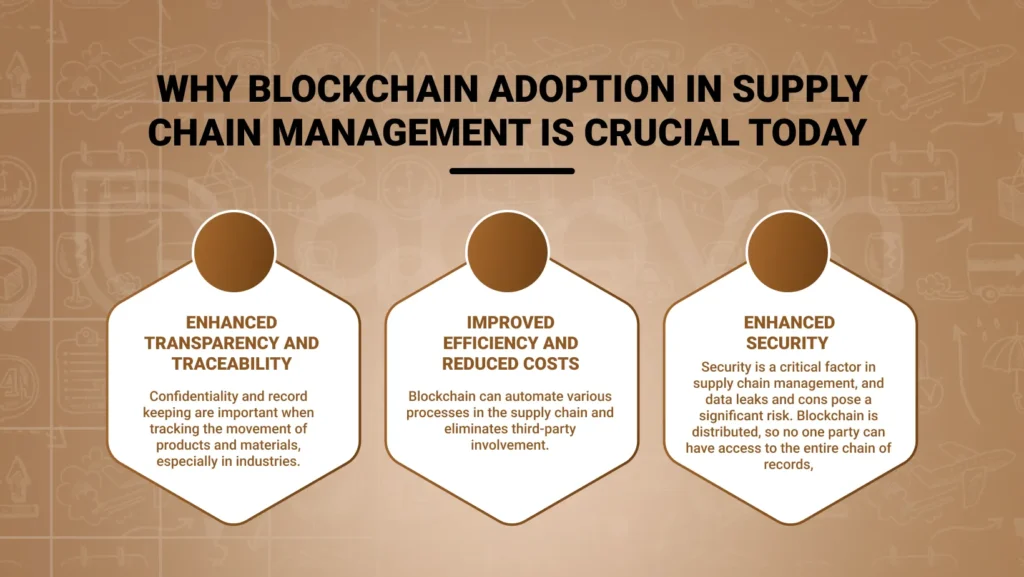
Why Blockchain Adoption in Supply Chain Management Is Crucial Today
Given its roots in virtual currency, it’s crucial to recognize blockchain’s broader implications. Among various fields, supply chain management stands out as highly promising for blockchain’s application. Key features like decentralization, immutability, and transparency make blockchain ideal for solving supply chain issues.
Moreover, in this section, we explore the necessity of blockchain in supply chain management today, highlighting enhanced visibility and accountability, improved efficiency and cost savings, enhanced security, compliance, and governance, bolstered interactions and trust, increased sustainability, and real-time tracking and alerts.
Enhanced Transparency and Traceability:
Confidentiality and record keeping are important when tracking the movement of products and materials, especially in industries. It requires product sources and authenticities such as food, drugs, and designer products industries. Blockchain presents an authenticated database where the tracking of every supply chain activity is stored. This ledger is available only for admitted individuals and every stage of the supply chain is visible and corroborated.
Consequently, Blockchain finds application in the food industry by tracking a product’s journey from farm to consumer, showcasing every process it undergoes. This transparency enables swift responses to issues like contamination or recalls, ensuring customer safety and brand reputation preservation.
Improved Efficiency and Reduced Costs:
Blockchain can automate various processes in the supply chain and eliminates third-party involvement. In traditional supply chain systems, there are many intermediate dealers which increases the complexity and expense. Through using the blockchain, it is possible to get rid of these middlemen since there is a single source of truth.
Smart contracts are digital contracts that automatically execute terms, like fund transfers or quality checks. For example, they can pay a supplier upon goods verification, streamlining paperwork, reducing errors, and speeding up transactions. Thus, it translates to huge cost savings and enhanced efficiency.
Enhanced Security:
Security is a critical factor in supply chain management, and data leaks and cons pose a significant risk. Blockchain is distributed, so no one party can have access to the entire chain of records, making it less vulnerable to hacking or modifications. Every business on the blockchain has a unique cipher, and it links up to the previous transaction block to form a series of blockages the tampering with this block is almost impossible.
Furthermore, blockchain guarantees data immutability, meaning no one can alter or delete data once written.
This is crucial to maintain record integrity and equitable information access.
Use Cases for Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Blockchain finds multiple applications in supply chain management, particularly in enhancing traceability and transparency and promoting environmentally and ethically sustainable practices.
Traceability and Transparency
Ensuring Product Authenticity:
Blockchain in the supply chain ensures a seamless chain of custody from manufacturing to purchase, as product authenticity can be readily verified.
For instance, in the pharmaceutical industry, follows each process right from the production of drugs and guarantees potency and quality.
Enhancing Food Safety:
A notable real-world example of blockchain is in the food industry, where it traces products from manufacturers to consumers, aiding in identifying contamination sources and facilitating product recalls to protect consumers and minimize business losses.
Improving Recall Efficiency:
In the recall scenario, blockchain improves recall procedures due to the enhanced accuracy of tracing. In the automotive industry, it keeps track of parts, from the manufacturer to the end distributor and consumer to enable organized and precise recall.
Environmental and Ethical Sustainability
Verifying Sustainable Practices:
Blockchain captures sustainable initiatives all through the production process right from the procurement. In fashion, it monitors environmental management systems of suppliers and informs consumers regarding sustainability information.
Ensuring Ethical Sourcing:
Blockchain provides a record of labor practices and certifications that are secure and can be easily audited. In the coffee industry, it follows beans from the farm to the cup and helps to support better labor practices and social justice.
Reducing Environmental Footprint:
Providing detailed insights into power consumption and CO2 emissions, blockchain empowers businesses to improve supply chain efficiency, reducing fuel loss, greenhouse gas emissions, and costs simultaneously.
Promoting Circular Economy:
Thus, blockchain in recycling and reuse helps in tracking the product life cycle. They apply it in electronics where it helps identify reusable components thus encouraging the recycling of used ones.
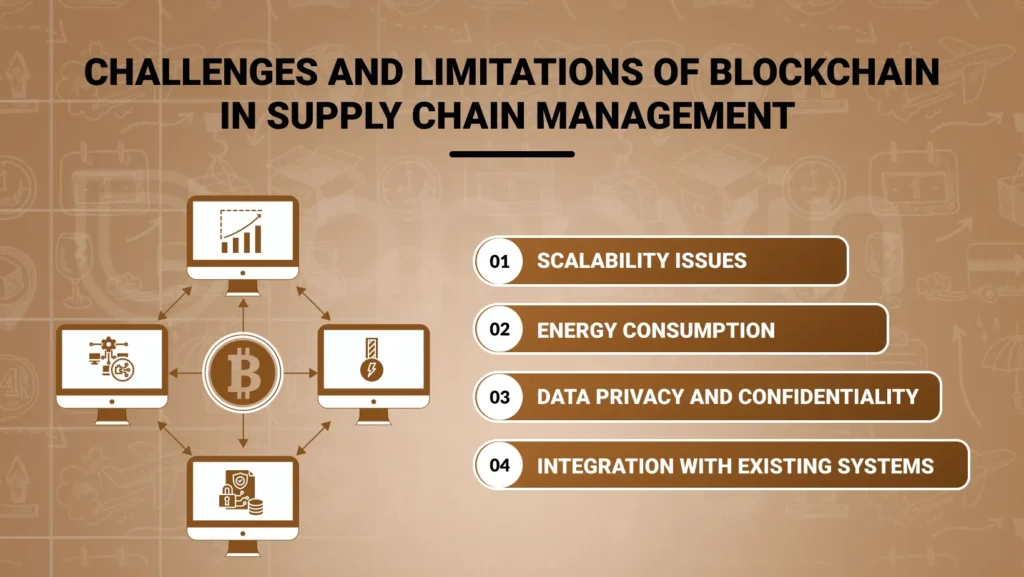
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Scalability Issues:
The main drawback of employing blockchain in SCM is the scalability issue. Traditional supply chains handle vast amounts of information and transactions daily, posing a challenge for modern blockchains to process the data influx in real-time.
Energy Consumption:
Moreover, the proof-of-work version of blockchain is notorious for its high energy consumption levels. Mining, the process of verifying transactions on the blockchain network through solving complex mathematical problems, requires significant resources and consumes immense power. This drawback is exacerbated by industries’ ongoing efforts to reduce their environmental impact.
Integration with Existing Systems:
Additionally, deploying blockchain in supply chain management presents another challenge: compatibility with existing SCM systems. Integrating these systems seamlessly into a new blockchain platform is a complex endeavor that requires significant investment of time, money, and resources. Moreover, internal resistance to adopting new technologies within the organization may further hinder integration processes.
Data Privacy and Confidentiality:
Conversely, the public nature of information stored in a blockchain can pose a disadvantage in certain situations, such as data privacy or confidentiality concerns. Supply chains encompass various details, including administrative, financial, and strategic data that organizations may prefer to keep undisclosed.
How To Implement Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Here are several strategic steps that need to be considered while integrating blockchain into supply chain management. These consist of product tracking and tracing, logistics transparency, smart contracts, and others.
Product Tracking and Traceability:
We can regard product tracking and traceability as key values of blockchain-based systems. Similarly, the blockchain records and verifies the unique attributes of each product or batch. For example, in the American food industry, blockchain offers an immutable record of product history, origin, and lifecycle, aiding in contamination prevention and response.
Supply Chain Transparency:
Most participants in this supply chain model will include manufacturers, suppliers, logistics providers, retailers, and customers. Organizations must prioritize transparency to foster new relationships and enable efficient decision-making processes. For instance, in the pharmaceutical sector, blockchain’s distributed ledger can track drug manufacturing and distribution, ensuring regulatory compliance and safety by eliminating counterfeit products.
Smart Contracts:
Moreover, it is essentially a programmed agreement that automatically executes contract terms without third-party intervention. At the operational level, smart contracts applied in supply chain management enhance efficiency in various processes. For example, by implementing a smart contract mechanism, payment to a supplier is contingent upon delivery confirmation and shipment authenticity, as confirmed by the program. Additionally, it can automatically trigger ownership transfer or other actions based on predetermined conditions or events. This automation reduces reliance on intermediaries, streamlines procedures, and minimizes the likelihood of errors or conflicts.
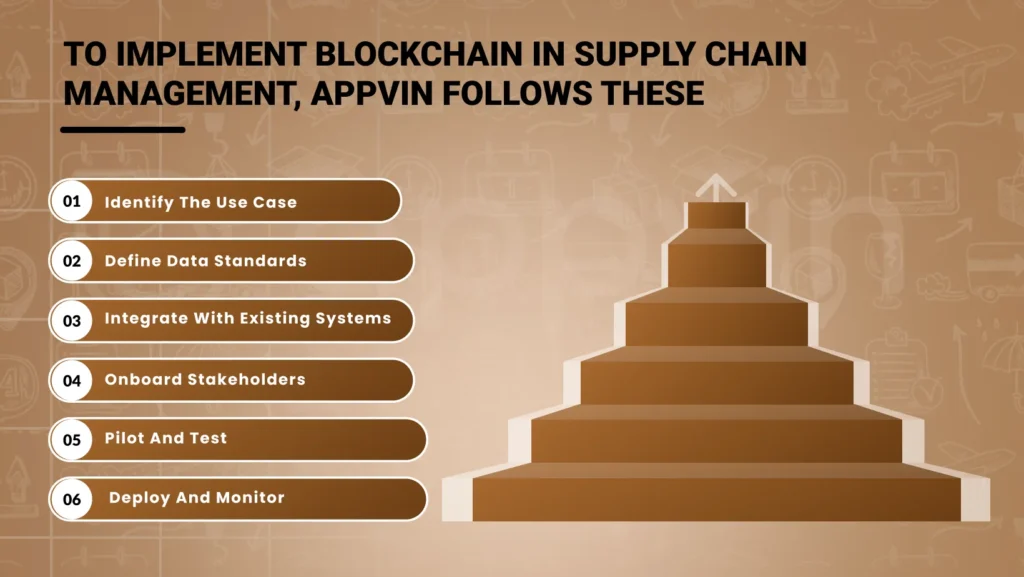
To implement blockchain in supply chain management, AppVin follows these steps
We must note that implementing blockchain technology in supply chain management greatly benefits by enabling better, more secure, and modern supply chain solutions.
To achieve this at AppVin, we employ the following flowchart to ensure that we implement blockchain solutions in supply chain management appropriately. It will also clarify use cases, define datasets, fit into existing systems, populate all the relevant stakeholders, test the solution, and monitor our progress.
Identify the Use Case:
We need to establish the initial use of blockchain in supply chain management by outlining specific areas where a particular supply chain could benefit from its implementation.
Furthermore, to help the readers better understand AppVin’s approach, it is important to first explain how we evaluate potential opportunities for blockchain. Common use cases include:
– Improving the product identification and information
– Made with the aim of increasing the efficiency of the recalls.
– This is also very important in verifying the authenticity of the products in the respective market.
– Verifying compliance with the requirements set by various laws and standards in the procurement of goods and services
– Optimizing inventory management
This way, with meticulous outlining of exact requirements and possible advantages, it would be possible to adapt the given blockchain solution to the needs of the identified supply chain.
Define Data Standards:
However, after understanding the use case, the next step is to standardize the formats of data to be collected. This is the case because all the records stored within the blockchain should have the same data format to securely manage the system. At AppVin, we:
– Develop guidelines for major data formats and understanding for registration of supply chain events and information.
– Make sure that all the fields such as time of the event, product identification, and even some of the transactional information are also normalized.
– Engage with standard and formal practice with the industry and set laws so that it can be aligned with legal and standard considerations.
Integrate with Existing Systems:
One of the most important steps is to incorporate the blockchain solution into the supply chain management applications currently used.
Understand the current systems and architectures and determine where integration should occur.
– Working with IT and operation specialists to connect blockchain to other systems such as ERP, WMS, and other relevant systems.
– The ability to integrate the blockchain solution with other systems to enable information sharing and real-time updates.
It is imperative to maintain continuity and improve the performance of active supply chain processes.
Onboard Stakeholders:
Blockchain is effective only if all the relevant stakeholders engage in the implementation process.
- Enumerate all stakeholders involved in the system, including suppliers, manufacturers, logistics companies, retailers, government, and other authorities.
- Arrange meetings and seminars to address concerns and enhance stakeholders’ understanding of blockchain solutions’ applications and operations.
- Establish effective communication channels and encourage reporting or discussion of any issues to foster a strong working relationship.
By engaging stakeholders in this manner, they become invested in implementing the blockchain solution, contributing to its development.
Pilot and Test:
Finally, it is crucial to implement the blockchain solution for a limited number of uses and monitor it to determine possible challenges before going to the public. AppVin’s approach includes:
– Deciding to implement the system on a selected short supply chain as the initial phase of the pilot.
– Evaluating the effectiveness and stability of the implemented blockchain solution in a real environment.
– The process of reviewing feedback from all the stakeholders who participated in the pilot.
– Examining the data for any signs of bottlenecks, threats or other problems with performance, safety, and usability.
Deploy and monitor:
Lastly, the concept of the solution implemented after pilot testing and data validation is to deploy the blockchain technology on a large scale to be continually monitored. At AppVin, we:
– Introduce the blockchain solution in every link within the supply chain network.
– Regular training should be offered to make sure that this adoption is effective and that the various aspects of it can be run efficiently.
– Consequently, put in place the monitors to enable real-time monitoring of the effectiveness of the blockchain solution.
– Periodically check existing libraries and update them to maintain the most protection, functionality, and compliance possible with new defenses, optimizations, and policies.
Conclusion
If you want to implement blockchain in your next supply chain management project, contact AppVin Technologies. We are the best cross-platform app development company, and we will help you with blockchain services that help companies harness the power of blockchain with real-world applications from the leaders in distributed ledger technology. Blockchain technology holds transformative potential for supply chain management, and as the standards evolve, it has the potential to become an integral part of modern supply chains. Contact us today to explore how blockchain can revolutionize your supply chain processes.
FAQs
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. It ensures data clarity, security, and consistency, making it ideal for applications that require reliable, immutable records.
How does blockchain improve supply chain transparency?
Blockchain improves supply chain transparency by providing a single, immutable record of all transactions accessible to all stakeholders in the supply chain. This visibility ensures that every step in the supply chain is transparent, traceable and verifiable.
What are smart contracts and how do they work in supply chain management?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts where the terms of the contract are written directly into law. In supply chain management, arrangements such as payment and transfer of ownership are carried out based on predetermined conditions, reducing the need for intermediaries and reducing error.
What steps should be taken to implement blockchain in supply chain management?
1. Identify a specific application.
2. Choose the right blockchain platform.
3. Define data values.
4. Participate in existing programs.
5. All relevant stakeholders on board.
6. Conduct pilot tests.
7. Implement the solution and continuously monitor its performance.
Can blockchain technology be integrated with existing supply chain systems?
Yes, blockchain technology can be integrated into existing systems such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) and warehouse management systems (WMS). This integration is essential for seamless data flow and process automation.