Businesses are tapping into technology more and more as a tactic to enhance their operations. Utilizing top-notch, Logistics and Supply Chain Management (SCM) methods and merging them with these technologies can yield impressive results for your business, like cutting costs, boosting income, and slicing down the time-to-value.
Companies are incorporating tech into their supply chains and logistics routes to keep up with trading trends. This helps ensure modern business success. In the continuously changing world of supply chain management, the use of tech becomes even more important. It’s vital for efficiently tracking and making decisions based on timely data.
Software for supply chain management is centered on managing and enhancing the sharing of information among various principal supply chain cohorts to obtain the following outcomes:
- Just-in-Time Procurement.
- Reduction of Inventory.
- Increasing Manufacturing Efficiency.
- Fulfil customer Needs Quickly and Easily.
- Cross-functional Supply Chain Solutions.
With the help of advanced technology in supply chain management, companies are now putting up supply chain solutions that accelerate processes and eliminate supply chain bottlenecks. These technology solutions allow companies to achieve some degree of on-demand (or customization) during the production cycle.
Here in this article, we’ll explore the role of technologies in supply chain management and the advanced technologies used to enhance the performance of mobile apps for supply chain management. These technologies are the following:
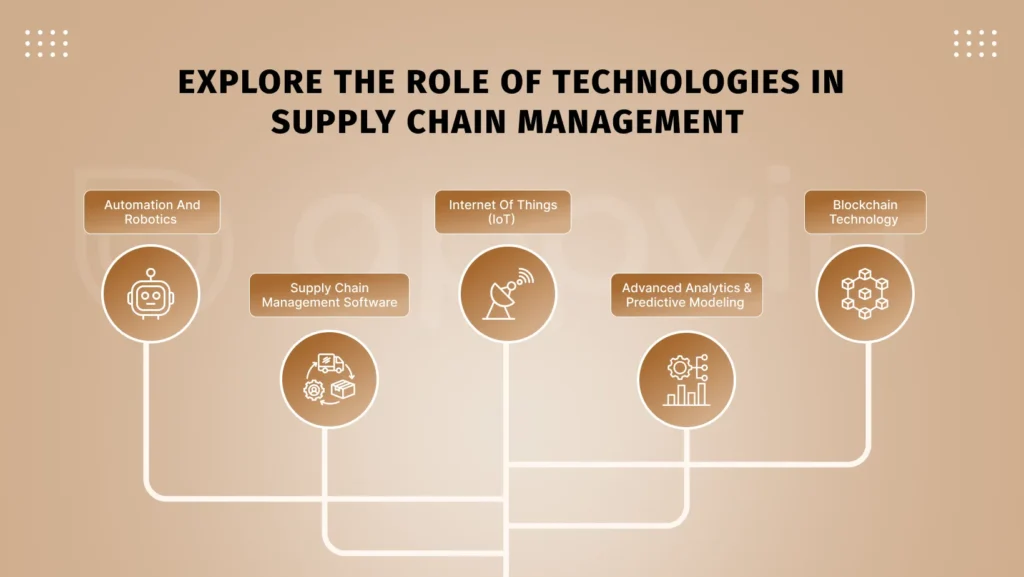
Explore the role of technologies in supply chain management
Automation and Robotics :
Advanced analytics uses strong tools that aid companies in improving strategic choices, augmenting operations, skyrocketing growth, and boosting profits. It is a widespread term that includes multiple data examining tools mainly used for predicting, like machine learning (ML), predictive modelling (PML), neural networks and artificial intelligence (AI).
Primarily, companies use these analytics not merely for business knowledge but to predict future scenarios and for making guided decisions. Robots have always been big in supply chain technology. Industries use them to move stuff in storage and handle orders.
But, as AI advances technology, machines will be able to take over the manual, human-dependent tasks, from order picking and packing, to order fulfillment technology.
Supply Chain Management Software (e.g., ERP Systems):
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is software that automates, streamlines and optimizes critical business processes. ERP software for your supply chain management requires integrated processes, data models, and data to synchronize information across your internal business function and simulate your supply chain in real time.
An ERP system is a tool for collecting all your organization’s financial information, supply chain information, operations information, commerce information, reporting information, manufacturing information, technology in supply chain management, and HR information into one place. That way, your leaders can see a complete picture of your business without having to consult multiple sources and figure out how the components might interact with each other. The use of ERP development in your supply chain system is especially important. After all, it saves you time and money because it streamlines your operations, which means you don’t have to manually update the information every time you need to do inventory management. Modern supply chain ERP modules also include digital solutions like dashboards and business intelligence, as well as IoT technology.
Internet of Things (IoT):
IoT has tangibly transformed the supply chain by connecting end-to-end objects to the internet, allowing IoT devices to be filtered by sensors or RFID tags. It collects data and allows for real-time monitoring throughout the entire supply chain. Not only does this improve inventory management, but it also makes it easier to make quick decisions in dynamic environments.
However, manufacturers and transportation companies can expect to invest in IoT deployments, especially to support manufacturing operations, monitoring production assets, and managing freight fleets. As IoT enables location tracking, weather monitoring, traffic monitoring, etc., companies will be looking to integrate IoT and AI into the supply chain management process for a variety of applications. For instance, based on this information, suppliers can redirect a delivery to a local distribution centre or send a repair team to address a real-time issue.
Advanced Analytics and Predictive Modeling:
Advanced analytics includes a wide range of powerful tools that help businesses make better strategic decisions to enhance operations, growth, and profitability.
Additionally, advanced analytics refers to several data analysis tools, mainly used for predicting things. These include machine learning (ML), predictive modelling (PML), technology in supply chain management neural networks, and artificial intelligence (AI). Companies use these analytics to guess future results and aid their choices, not only for business insights.
Blockchain Technology:
Companies depend on data, the quicker and more correct it is, the greater its worth. Blockchain is an ideal technology for this, offering immediate, widespread, visible information stored on a blockchain ledger. Only approved network members can see this ledger. A blockchain network can track orders and payments, accounts and production, and more. The technology works on a set of transactions that are best suited to trace the source of goods and build trust in supplier data and supply chain operations.
In addition, blockchain’s immutability plays a key role in the supply chain management ecosystem, as it establishes an audit trail that’s much more effective than traditional tracking methods such as email or bookkeeping.
Moreover, this is the biggest blockchain example in terms of enabling track and trace use cases that allow businesses to investigate the custody of goods. This helps identify counterfeit items and instances of fraud, highlights the most vulnerable suppliers, ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, and builds transparency about the origin and movement of goods.
Cloud Computing:
Utilizing cloud-based communication, supply chain stakeholders can communicate and collaborate in real-time. This helps the supplier, maker, mover, and seller share useful information fast. It makes supply chains easier for everyone to see what’s happening, which means faster reactions to changes in demand or supply.
Furthermore, it cuts down waiting time, and stock levels and makes sure there’s just enough supply for everyone in the chain. Key tech like artificial intelligence (AI), predictive analytics, and machine learning make warehouses automated. It speeds up delivery, manages stock, improves sourcing relationships, and makes new user experiences that boost sales. AI has changed the way we predict demand and make decisions in the supply chain. A combination of technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), predictive analytics (Predictive Analytics) and machine learning, automates warehouse operations, improves delivery time, proactively manages inventory, optimizes sourcing relationships and creates new experiences that enhance user experience and increase sales.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized demand forecasting and supply chain decision-making, enabling AI algorithms to analyze vast volumes of data to identify patterns, anomalies and predictive requirements that traditional methods cannot.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
Many tech gadgets, such as AI, forward-looking assessment, and learning machines, help update warehouse duties, quicken delivery, skillfully handle stock, refine supplier relations, and develop fresh experiences to elevate user joy and grow sales. AI holds a significant role in handling supply chains, notably in forecasting demand and decision-making. AI-powered decision-making systems improve supply chain management by proactively adjusting inventory levels, routes and production schedules to respond to changing conditions. This flexibility increases overall flexibility and capacity to meet market demand.
Data Integration and Connectivity:
Supply chain mobile apps benefit from data integration and connectivity tech. Consequently, they gather data from different systems and people in the supply chain network. Sources like ERP systems, warehouse managers, and IoT devices feed data into these apps. This gives a full, up to date view of the supply chain. Everyone can see the latest inventory, order, and shipment tracking info. This means they can make smart choices based on real facts. Plus, it makes working together simpler.
Sharing data on mobile platforms means everyone’s in the know. Predictive analytics, driven by the data, forecast demand and size up risks. It smooths out order management by taking care of processing, tracking, and filling orders. So, this tech is crucial for the best supply chain operations, visibility, and efficiency.
Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring:
In addition, mobile apps can track shipments. Users get updates on where shipments are, how they’re doing, and when they’ll arrive. This helps make decisions and step in if things go wrong. Moreover, real-time tracking makes things run smoother, stops stock from running out, and makes customers happy with deliveries on time. Plus, real-time tracking helps manage supply chains better. It finds the best routes, cuts shipping costs, and better organizes resources. Checking real-time data like where vehicles are, traffic, and delivery times helps find and fix problems. In turn, jobs get done better overall. It also helps keep to rules and standards. Real-time monitoring gives right-now info about how products are handled and stored. So, it’s easier to keep things safe, stop products from going bad or getting damaged, and keep quality high through the supply chain.
Collaborative Platforms and Digital Marketplaces:
Furthermore, digital marketplaces and collaborative platforms have revamped the world of supply chain management, mainly through their use in mobile apps. These tools make communication, collaboration, and transactions between the different parties in the supply chain network a breeze.
Here’s how supply chain management benefits from mobile apps powered by these tech advancements:
Effective Communication:
Collaborative platforms in mobile apps spark instant communication among suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. Everyone can quickly handle issues, plan activities, and share critical info through instant messages and updates. This boosts productivity and responsiveness.
Better Collaboration:
Mobile apps with digital marketplaces offer a shared space for parties to work together on sourcing, buying, and managing inventory. Suppliers display their products while buyers can easily browse, compare, and order. This openness shortens delivery time and builds stronger relationships in the supply chain.
Smart Procurement:
Mobile apps with digital marketplaces make procurement transparent and smooth. However, buyers can browse various suppliers and products, compare costs and details, and make smart buying decisions on the fly. Plus, features like automated approvals and tracking make procurement efficient and precise.
Conclusion
In conclusion, technology plays a critical role in supply chain modernization. Every technological innovation from data analytics to the Internet of Things (IoT) disrupts the supply chain and artificial intelligence (AI) adds up to more efficient, faster, and more sustainable supply chains. Looking ahead, constant innovation and continuing innovation in technology will define the next frontier in supply chain management, opening new opportunities and driving sustainable growth. However, with proactive strategies and a flexible mindset, they can thrive in this fast-paced industry. The key to success in today’s world is to use different sources, choose the right routes, fund technology, build skills, stay within the best laws, provide better service to our clients, and stay ahead of global trade trends. The secret to success is to be innovative, resilient, and put our customers first.
FAQs
What is the role of technology in the supply chain industry?
Companies are incorporating tech into their supply chains and logistics routes to keep up with trading trends. This helps ensure modern business success. In the continuously changing world of supply chain management, the use of tech becomes even more important. It’s vital for efficiently tracking and making decisions based on timely data.
Software for supply chain management is centered on managing and enhancing the sharing of information among various principal supply chain cohorts to obtain the following outcomes:
- Just-in-Time Procurement.
- Reduction of Inventory.
- Increasing Manufacturing Efficiency.
- Fulfil customer Needs Quickly and Easily.
- Cross-functional Supply Chain Solutions.
Is technology making supply chain management more complex?
Even though tech brings fresh issues like digital security and combining tasks, it also delivers answers to make procedures smoother, boost clarity, and step up total effectiveness. If we plan and use it rightly, tech can uncomplicate logistics managing and propel company achievement.
How can companies overcome integration issues when implementing new technology?
Being slow to change and not fully grasping new tech can mess with introducing a complete solution. Deep-dive learning sessions and encouraging a flexible mindset are key to beating this issue.
However, firms can tackle the problem of merging systems together. They can do this by putting money into ones that work well together. Doing lots of checks can help too. It’s also vital to train everyone well. Lastly, working with tech sellers and partners can make a big difference.
What are the risks associated with technology in supply chain management?
Risks with technologies include cybersecurity threats, data breaches, system failures, and integration challenges. However, these risks can be overcome through robust security measures, regular maintenance, and risk management strategies.