Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in supply chains, leveraging its high data processing capabilities, analytics, and automation tools to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of existing systems. AI and machine leaning in supply chain handles more data in comparison to humans and can demonstrate information, trends, relationships etc. This leads to better decision-making and enhanced efficiency. Advanced technology in supply chains holds great potential to positively impact sustainability goals and efforts to reduce the environmental impact of supply chains.
Sustainability is a concept that defines ethical purchasing, labour relations, energy and water resources preservation. Moreover, it balances the consumption of natural resources. Businesses are waking up to the fact that sustainability is not just another compliance issue. Techniques like AI and machine leaning in supply chain can sustainably optimize supply chains. Specifically, these technologies enable firms to gain analytical insights, thereby improving supply chain network designs, policies, and logistics. Moreover, a research paper on IEEE EXPLORE shows firms adopting Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) and Decision Trees to assess and enhance supply chain sustainability across economic, social, and environmental factors.
As supply chain digital highlighted, AI fosters collaboration between companies and thus improves sustainability within the supply chain networks. It allows organizations to collaborate and share crucial information, thereby enabling well-coordinated, informed decisions. Additionally, this article explores AI’s multifaceted impact on sustainable supply chain management, outlining advantages, implementation strategies, challenges, and prospects, and addressing common queries.
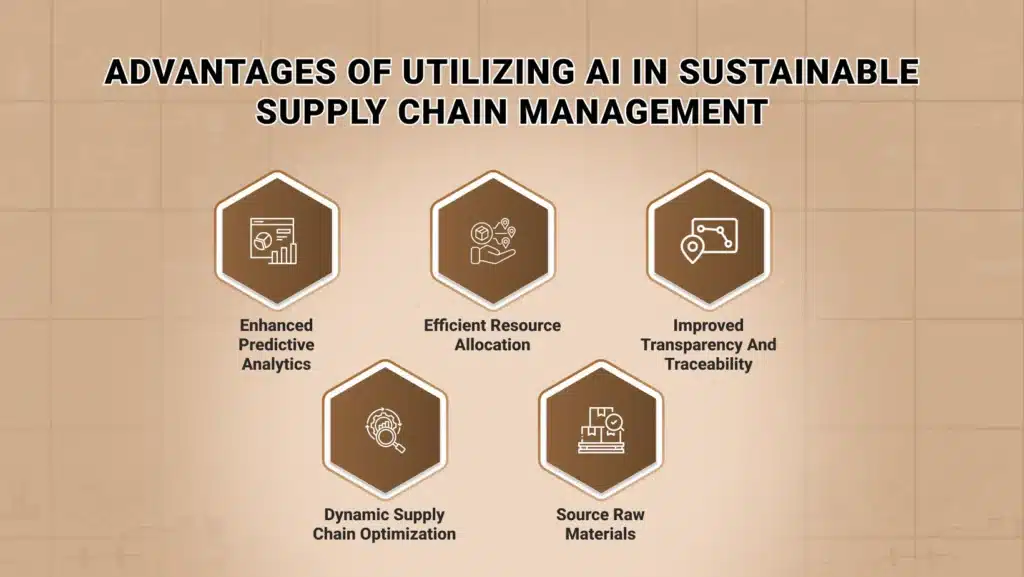
Advantages of Utilizing AI in Sustainable Supply Chain Management
The adoption of AI and machine leaning in supply chain provides several distinct advantages that contribute to sustainability. Firstly, the integration of AI in the management of supply chains presents several distinct benefits that should be viewed as contributing to sustainability:
Enhanced Predictive Analytics
Based on consumption patterns, companies can avoid bulk inventory purchases while still meeting consumer demand as it arises. Moreover, it makes economic sense as it eliminates wastage from excess stock.
Efficient Resource Allocation
AI, through prescriptive analysis using big data, learns, predicts, and troubleshoots resource consumption. Consequently, firms can reduce CO2 emissions through daily management of transport, production networks, and power usage.
Improved Transparency and Traceability
Some AI technologies, such as blockchain and IoT, provide an opportunity to track products from the manufacturer to the final buyer. Consequently, this transparency is valuable in examining product stability, ensuring compliance with environmental legislation, and establishing product reliability for customers.
Dynamic Supply Chain Optimization
As we know, supply chain processes may undergo many changes due to spontaneous events such as natural disasters or market trends. Employing AI, which can monitor and adjust activities in real-time, allows for immediate adjustments to expected or unexpected changes. Consequently, this agility helps unlock desired sustainability goals even when negative contingencies arise.
Source Raw Materials
In supply chains, especially in the procurement of raw products or data centre equipment and services, AI has enhanced efficiency. For instance, through predictive analytics, AI systems can forecast demand levels, enabling manufacturers to get supplies on time to meet required demand. Additionally, AI tracks supplier performance, identifying whether it meets set quality and quantity parameters. This concept also eliminates downtime and enhances the reliability of the whole supply chain system. In this regard, intuitive procurement is the use of AI as a way of automating various procurement chores. It minimizes transaction costs and human interventions hence reducing error rates in procuring raw materials.
Reduce Risk
As stated above, machine learning and other techniques in various forms allow AI systems to analyze multiple risks at once. It allows organizations to create extensive contingency real-time plans and refine risk management measures. For instance, the applications of AI in manufacturing processes, stock quantity, customer demand, and supply systems. This is because the effects of a chain of damage can be quantified to assess the level of harm done, leading to quicker identification of damages and efforts to minimize such advancements.
Moreover, automated supply chain tools constantly scan for threats and opportunities, often specifying them in real time to improve supplier relationships, actual and forecasted demand, transportation disruptions, and regulatory shifts. This practical assessment empowers action before potential problems arise and allows for prompt intervention, thus limiting the effect on performance.
Implementing sustainable practices in your supply chain through AI requires
addressing sustainability within the framework of supply chain strategy, with technology as an enabler of change.
The following are some steps that help to achieve sustainability in the supply chain.
Data Integration and Analysis:
This can be done systematically by aggregating customer data from multiple points throughout the supply chain. This involves data from suppliers, using it in the production line, its delivery to other centers, and its consumption by consumers. It can also be utilized to capture further information that is then analyzed through sophisticated AI methods to diagnose potential problems and discover opportunities for enhancement.
Supplier Collaboration:
It can also involve the development of a close relationship between the shareholders and the suppliers to ensure that the latter embraces environmentally friendly practices. Supply chain management can assist in evaluating the overall performance of those suppliers and their sustainability standing, making it simpler for end companies to identify their ideal business partners based on their concerns for the environment.
Process Optimization:
Introduce AI technologies to enhance the production line, cutting costs associated with unwanted outcomes, such as excessive waste or energy expenditures. For instance, it can possibly estimate when machinery is likely to break down and plan maintenance in a timely manner without much interference and energy use.
Smart Logistics:
Always pursue operational strategies and technologies focusing on logistics planning and minimal fuel usage. It may also improve the efficiency of utilization of the space and work in the warehouse by the automation of inventory checking, stock rotations, and restocking procedures.
Sustainable Product Design:
Since this study focuses on the design phase, then it means that applying AI to design can make the products. Easy to recycle or reuse. AI and machine leaning in supply chain run many simulations to determine various composite materials and their structures that will be best for saving the environment.
Monitoring and Reporting:
The following is a recommendation on how AI can be used in sustainability management: The information and data collected from the different levels of a supply chain should be constantly monitored for sustainability. Real-time data analysis ensures that the changes are promptly made and that all the operational processes meet the environmental legislation. It also helps in automating the flow of sustainability reports to the various stakeholders offering them clear and information concerning organizational sustainability.

Challenges of implementing AI for sustainability in Supply Chains
While the benefits of AI in sustainable supply chain management are clear, there are several challenges that businesses must navigate: While the benefits of AI in sustainable supply chain management are clear, there are several challenges that businesses must navigate:
Data Quality and Integration:
This is particularly important because when using artificial intelligence, proper data is crucial. One of the prevalent issues of many supply chains remains the scattered data and unequal data quality so that analytical insights are not precise enough.
High Implementation Costs:
The start-up costs involved in implementing Artificial Intelligence technology such as the hardware, software, and AI expertise may be rather expensive. These costs may be expensive to many small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) for one reason or the other.
Skills Gap:
Currently, there exists a shocking gap in the workforce regarding the skills underlying data and AI. Challenges that relate to workforce constraints for AI for sustainability projects include that it may be difficult for firms to source for or develop talents that will be useful in deploying sustainable AI programs.
Resistance to Change:
AI and sustainability measures are commonly a part of the company’s culture, so their implementation may be challenging. This is so since many employees and stakeholders are likely to resist the adoption of new technologies and processes.
Security and Privacy Concerns:
Artificial intelligence supply chains are characterized by the handling of comprehensive and intricate data. Preserving data, as well as its confidentiality is a crucial element of any enterprise as the number of cyber threats is constantly growing.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues:
It is obvious that engaging with different environmental legislations and implementing them can be somewhat of a daunting task. It is also important to understand that AI solutions should be able to cope with switching between different levels of compliance.
The Future of AI and Sustainability in Supply Chains
The future of AI and sustainability in supply chains looks promising, with several emerging trends poised to drive further advancements: The future of AI and sustainability in SCs is indeed bright, as there are several more trends evident to foster future development:
AI-Driven Circular Economy:
Hence, AI will be vital in improving recycling practices, managing product life cycles, and developing products that can be recycled repeatedly.
Blockchain Integration: AI & Blockchain:
The proposed combination will add more functionality in tracking and supplying an end-to-end solution to the supply chain system. This integration will result in better rates in certification of sustainability practices as compared to tracking from other sources such as third parties.
Advanced Robotics and Automation:
More robots and automation with artificial interfaces will be developed in the supply chain processes, resulting in higher productivity and fewer errors due to reduced human intervention. Additionally, these technologies will increase sustainability by reducing waste at the source and optimizing resource usage.
AI-Powered Decision Making:
Confidence is enhanced by AI algorithm upgrades, facilitating more informed decision-making in the supply chain. Consequently, businesses can manage profits while pursuing sustainable goals.
Sustainable logistics
AI revolutionizes transport by employing smart machines like vehicles and drones. These technologies reduce emissions and enhance efficiency in delivering parcels for courier companies.
Real-Time Sustainability Monitoring:
The discontinuities likely caused by AI and machine leaning in supply chain advancements will enable organizations to monitor environmental value across the supply network in real-time. Consequently, environmental challenges and opportunities will be clearly visible, facilitating the development of short-term solutions that demonstrate commitment to sustainable development.
Conclusion
Supply chain AI and sustainability are a perfect pair, combining to bring significant positive impacts to the environment and economy. While there are challenges to address, the benefits are substantial—such as increased effectiveness, reduced material usage, and greater openness and relevance. Overall, the advancement of technology through AI will be a key element in improving sustainable supply chain management, promoting sustainable development, and driving economic growth.
FAQs
How does AI technology enhance stability in the supply chain?
AI benefits sustainability through flexibility of resources and supply chain, risk mitigation and prediction, performance monitoring, transparency, and efficient logistics and energy usage.
Why, and how does Artificial Intelligence help in having a circular economy scheme in chains?
AI can also enhance recycling activity, help manage product lifecycle, and guide in the design of items that are simpler to recycle or redesign for reuse, which underpin circular economy strategies.
What is crucial to understand about blockchain within the context of sustainable supply chains and AI?
Blockchain, furthermore, enhances trust in sustainability tracking by employing decentralization and an immutable chain in supply chains. This ensures that only approved practices are executed, and that necessary checks and balances are followed in terms of sustainability.
How can small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) implement AI for sustainability in their supply chains?
To adopt AI-driven sustainability, SMEs can start with affordable and simple solutions that can be scaled up gradually. They can partner with technology providers to integrate AI alternatives in areas such as maintenance or logistics and progressively embed new sustainability practices.
What is the outlook for AI and sustainability in supply chains?
There is scope for a circular economy in the future with the development of AI, along with technologies such as Blockchain, Robotics and Automation, AI-driven decision-making, sustainable logistics solutions, and real-time sustainability performance checks.